
Difficulty swallowing in patients with GERD usually occurs due to inflammatory damage of the esophageal lining by the esophageal acid and its consequent narrowing or disruption of normal function peristalsis of the esophagus. In the cases when dysaphagia is accompanied by a rapid loss in body weight (over 10 kg for 3 months), or that is progressive, it represents an alarming symptom, due to fact that it is mainly caused by the tumor processes in the esophagus. Tumors of the esophagus and upper stomachĭifficulty swallowing can manifest exclusively for solid or liquid food, or as a combination of the two. Gastroesophageal reflux disease complicated by inflammatory narrowing of the esophagus Systemic diseases affecting the nerves that control the muscles of the pharynx and esophagusįunctional disorders of the esophagus (achalasia, diffuse spasm, diverticula, etc.)

Certain diseases can provide both types of dysphagia, so their careful evaluation and appropriate diagnostics are necessary.ĭysphagia is the dominant clinical symptom in most of the patients with diseases of the esophagus. This difference can be made with great certainty (80-85%) based on symptoms of patients themselves. The basis for the further treatment represents a decision whether the dysphagia is of oropharyngeal or esophageal origin. The sense of accumulation of food in the esophagus represents also another symptom that can occasionally occur in these patients. Accordingly, dysphagia represents a sense of inadequate passage of the swallowing contents. Conditions that may cause swallowing problems include nervous system disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or cerebral palsy esophageal problems, such as Heartburn, Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) stroke head or spinal cord injury or cancers of the head, neck or esophagus.Difficulty swallowing or dysphagia (Latin: dysphagia) is difficulty or feeling commencement of the act of swallowing (when it is called oropharyngeal or high dysphagia) or the feeling of the stopping of food and fluids in their passage from the UES to the stomach (esophageal, low dysphagia). Swallowing problems can happen at any age. Problems swallowing may also cause coughing or choking while eating, slow chewing or eating, gurgling sounds from the throat when eating, hiccups after swallowing and chest tightness or pain after swallowing. Other stomach conditions, such as peptic ulcers require medical attention.Ī person experiencing swallowing problems, which is called dysphagia, may have difficulty swallowing foods or liquids. These and other stomach problems may be treated with over-the-counter medications and lifestyle modifications, such as eating healthy, avoiding fatty foods and eating slowly. Common stomach ailments include Heartburn, Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), which occur when food and acids regurgitate and cause discomfort in the throat, chest or upper abdomen.
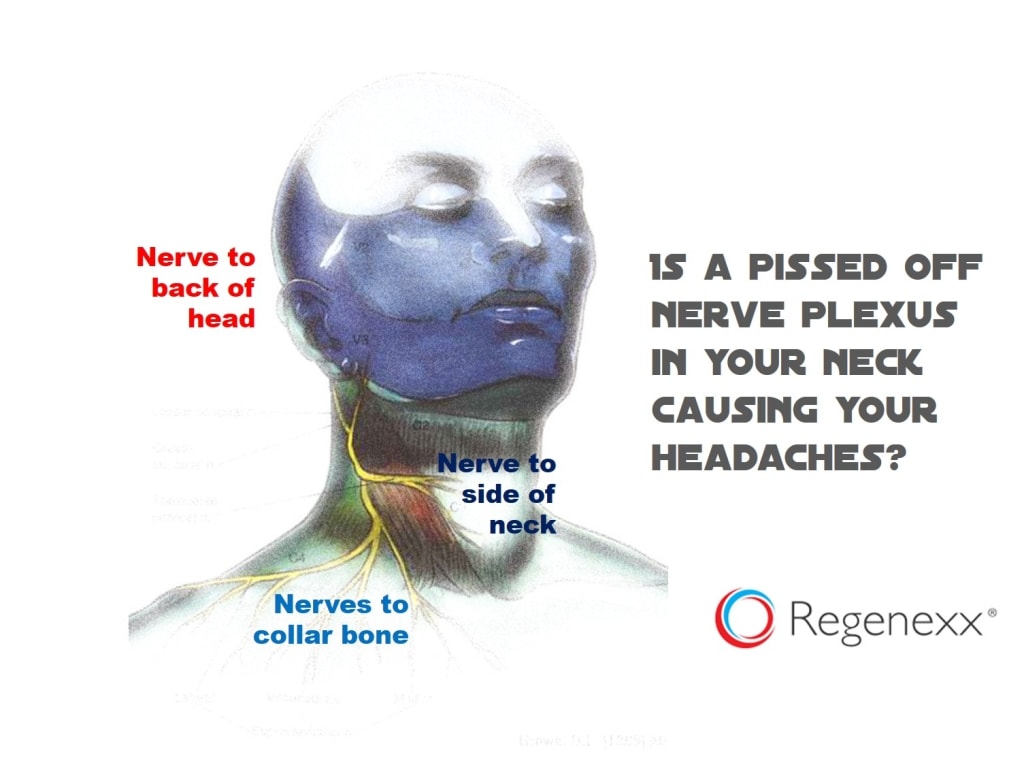

The stomach stores swallowed food, mixes food with acids for digestion and then transports the mixture to the small intestine. Most people have experienced some type of stomach problem or discomfort in their lifetime.
Find explanations, causes and treatments for common stomach problems and swallowing problems below:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
